Bruxism, or excessive teeth grinding or clenching, might seem like a minor health issue, but in fact, it can branch out and affect every aspect of our lives, from sleeping to eating to even performing at our job. We must promptly treat this serious health condition to prevent it from negatively impacting our lives.
What is Bruxism?
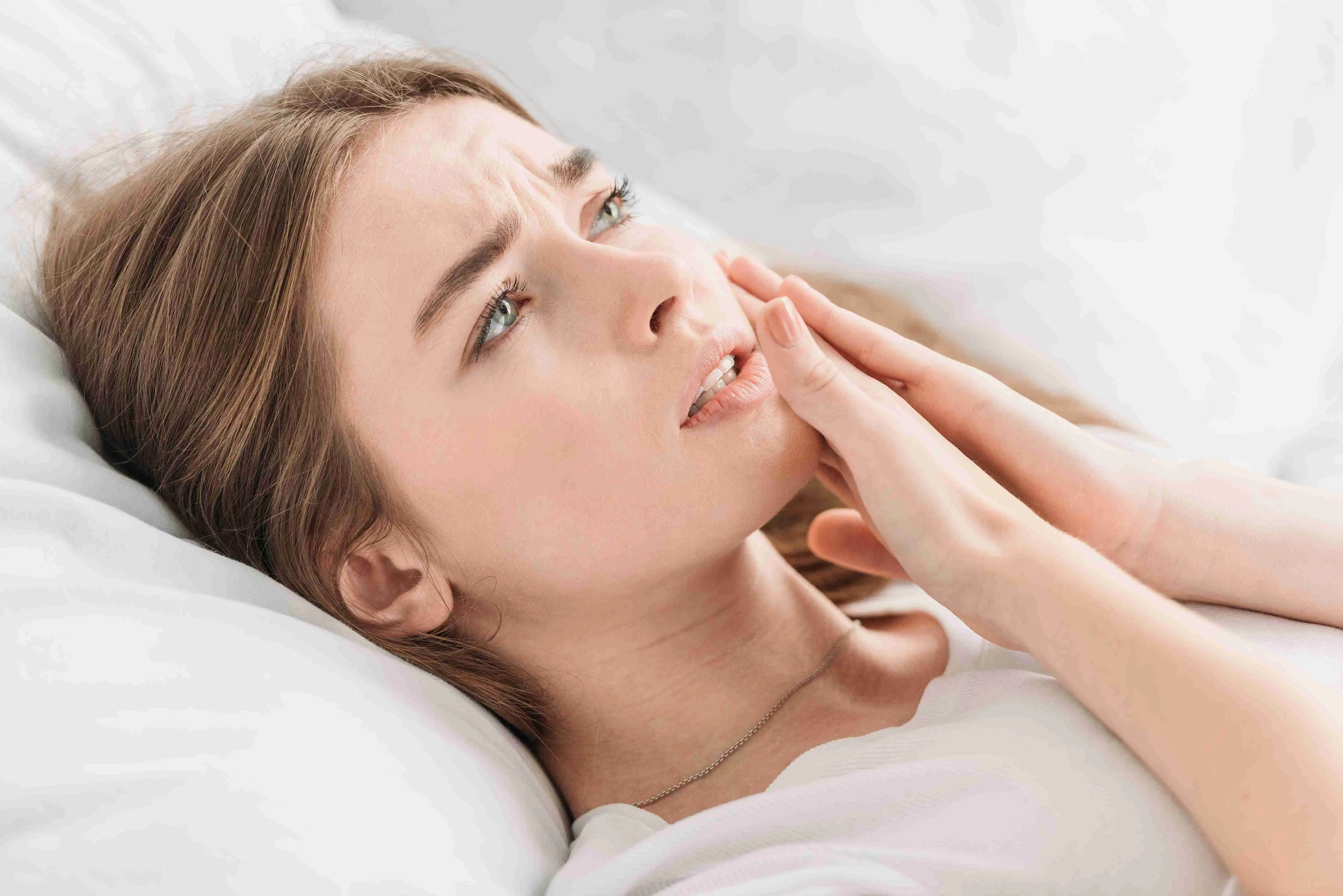

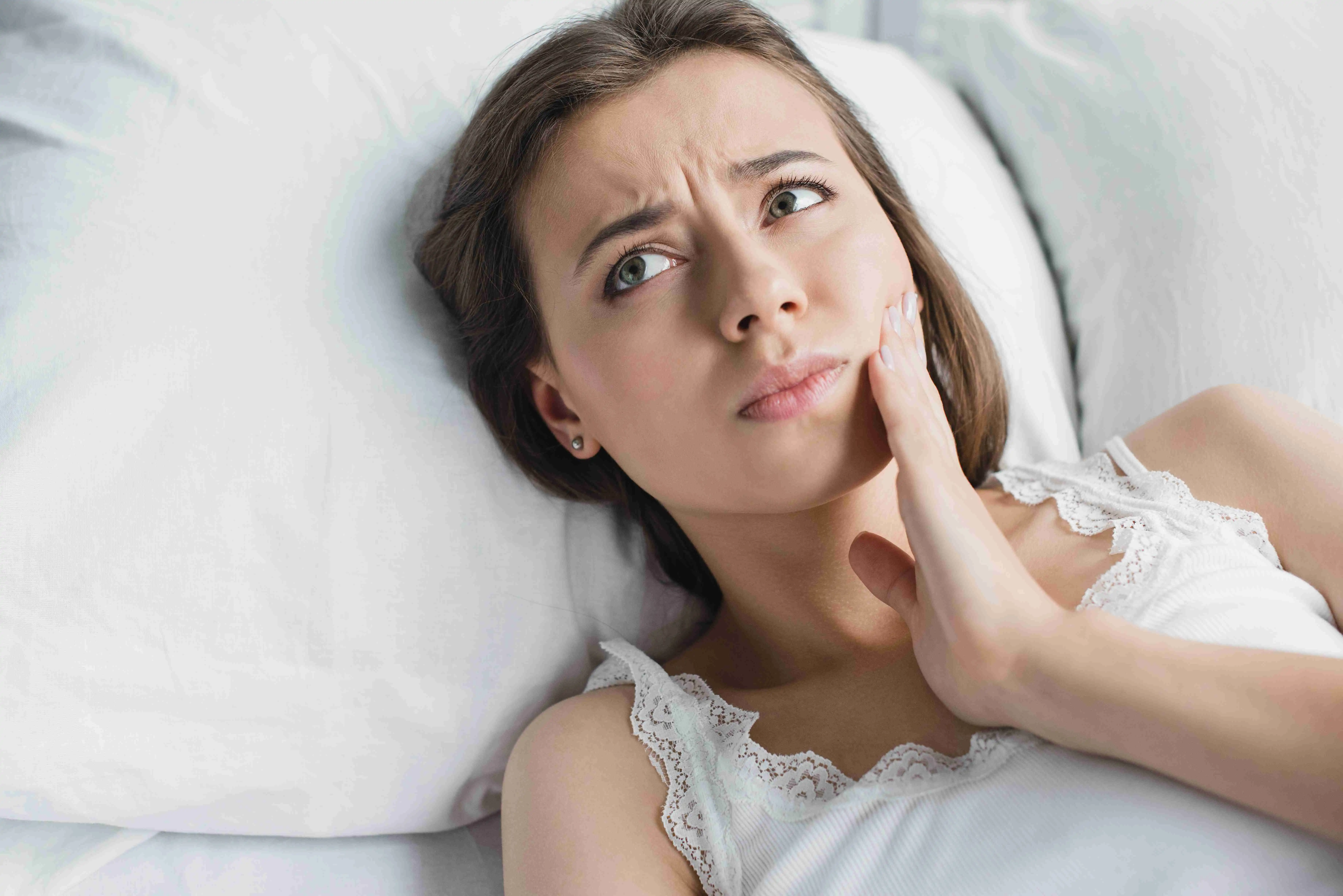
Bruxism is a condition characterized by excessive teeth grinding or clenching. It is a common dental problem that affects both children and adults. Although the exact cause of bruxism remains unknown, it is believed to be associated with stress, anxiety, and sleep disorders.
People with bruxism often grind their teeth unconsciously, usually during sleep. This can lead to a variety of symptoms, such as jaw pain, tooth sensitivity, headaches, and worn-down teeth. If left untreated, bruxism can cause serious dental problems and may require intervention from a dentist or oral specialist.
Symptoms of Bruxism
Bruxism symptoms can vary depending on many factors, such as how severe your bruxism is, your age, and other factors. The symptoms can range from headaches to damaged teeth, and it’s important to be able to identify them so you can take action and combat these symptoms.
Headaches
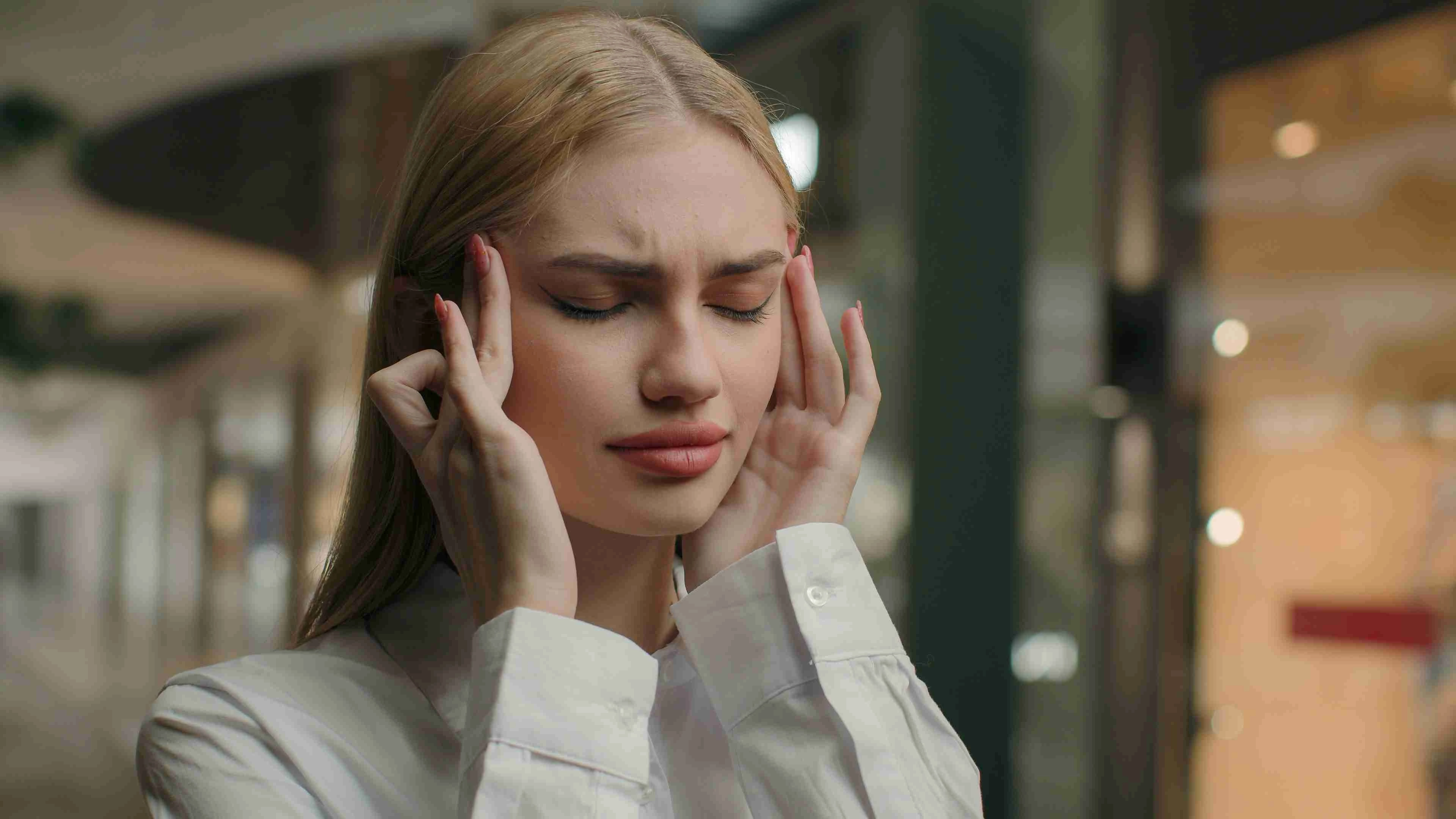

Individuals who grind their teeth may experience frequent headaches upon waking up in the morning. The constant pressure and tension placed on the jaw muscles can lead to tension headaches that can be quite debilitating.
Earache
The grinding motion of the teeth can put strain on the temporomandibular joint, which is located close to the ear. This can result in ear pain and discomfort, making it difficult for individuals to concentrate or go about their daily activities.
Tinnitus
Tinnitus, which refers to ringing or buzzing noises in the ears, is another symptom of bruxism. The constant grinding and clenching of the teeth can affect the temporomandibular joint, causing inflammation and irritation. This can then lead to the sensation of tinnitus.
Eating Difficulty
Individuals with bruxism may find it challenging to eat certain foods, particularly those that require extensive chewing. The pain and discomfort in the jaw muscles can make it difficult to move the jaw properly, resulting in a limited range of motion.
Jaw Pain or Stiffness
The continuous grinding motion can put excessive strain on the jaw muscles and joints, leading to soreness and discomfort. This can make it difficult for individuals to open their mouths fully or chew food properly.
Worn, Chipped, or Damaged teeth
Individuals suffering from bruxism often experience tooth sensitivity and pain due to the excessive force exerted on their teeth. The continuous grinding can wear down the enamel, leading to an increased and increased risk of cavities. In severe cases, bruxism can cause fractures or even tooth loss.
Causes of Bruxism
Several factors have been identified as potential causes. It is important for individuals experiencing symptoms of bruxism to seek professional dental care to prevent further damage and discomfort.
Anxiety
Individuals who experience high levels of stress and anxiety are more prone to grinding their teeth during sleep or even when awake. The subconscious release of tension through teeth grinding can provide temporary relief for those experiencing anxiety, but it ultimately leads to dental problems and discomfort.
Lifestyle habits
Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and caffeine consumption can also contribute to bruxism. These habits can disrupt normal sleep patterns and increase muscle tension, leading to teeth grinding during sleep. Additionally, individuals who have poor sleep hygiene or irregular sleep patterns are at a higher risk of developing bruxism.
Medications
Medications such as antidepressants, antipsychotics, and certain stimulants can increase the risk of teeth grinding. Individuals taking these medications should be aware of the potential side effects and consult their healthcare provider if they experience bruxism symptoms.
Malocclusion
Malocclusion, which refers to misalignment of the teeth or jaws, can also contribute to bruxism. When the teeth do not fit together properly, it can cause excessive pressure on certain teeth, leading to grinding or clenching.
Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by interrupted breathing during sleep, which can lead to fragmented and poor-quality sleep. It is believed that the clenching and grinding of teeth in bruxism may be the body's attempt to open up the airway and facilitate breathing.
The connection between sleep apnea and bruxism underscores the importance of addressing underlying sleep disorders in the management and treatment of bruxism.
Types of Bruxism
It’s a misconception that bruxism only occurs during sleep, as there are two types of bruxism: awake bruxism, which occurs while the individual is awake, and sleep bruxism, which is more common and occurs during sleep.
Awake Bruxism
Awake bruxism is when a person consciously or unconsciously clenches or grinds their teeth while awake. This type of bruxism is often associated with stress, anxiety, or tension. Additionally, certain habits, such as clenching the jaw or chewing on pens or pencils, can cause it.
Sleep Bruxism
Sleep bruxism, on the other hand, occurs during sleep and is more common than awake bruxism. It is often characterized by rhythmic contractions of the jaw muscles and grinding of the teeth. Sleep bruxism can occur in both children and adults and can be caused by various factors. Stress, anxiety, drinking, smoking, and some medications are just a few of the causes of sleep bruxism, which can affect both children and adults.
Complications If Bruxism Left Untreated
Both awake and sleep bruxism can have detrimental effects on oral health if left untreated. The constant grinding and clenching of the teeth can lead to dental damage. It can also cause temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders. Therefore, it is essential to seek professional help if you suspect you have bruxism.
Dental Damage
The constant clenching and grinding of teeth can wear down the enamel, causing tooth sensitivity, fractures, and even tooth loss. In severe cases, individuals may require extensive dental treatments such as crowns, bridges, or implants to restore their damaged teeth.
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorder
Another complication that can arise from untreated bruxism is temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ). The excessive strain placed on the jaw joint during teeth grinding can lead to inflammation and dysfunction of the TMJ.
This can result in jaw pain, difficulty opening and closing the mouth, and even locking of the jaw. TMJ disorder can significantly impact an individual's quality of life, making it difficult to eat, speak, and perform daily activities.
Chronic Headaches
The constant tension and pressure exerted on the muscles and joints of the face and head can lead to frequent headaches, particularly upon waking up in the morning. These headaches can range from mild to severe and may be accompanied by other symptoms such as neck pain and facial pain.
Facial Pain
The constant grinding and clenching of teeth can cause muscle fatigue and strain in the face, leading to facial pain. This pain may be felt in the temples, cheeks, or jaw area. Over time, the facial muscles may become tense and sore, making it uncomfortable to perform simple actions like chewing or talking.
Sleep Disorders
Bruxism often occurs during sleep, causing disruptions in sleep patterns and leading to sleep disorders such as insomnia or sleep apnea. The constant grinding and clenching can also result in restless sleep and frequent awakenings, further exacerbating the sleep disturbances.
These sleep disorders can have detrimental effects on overall health and well-being, impacting cognitive function and mood, and increasing the risk of developing other health conditions.
Treatments for Bruxism
Bruxism can be a serious issue for many people as it can disrupt their sleeping pattern, which will lead to further complications such as headaches and sleeping disorders, which will severely negatively impact your day-to-day life. Fortunately, there are several effective treatments available to help alleviate the symptoms of bruxism.
Mouth Guards
One commonly recommended treatment is the use of mouthguards. People wear these custom-fitted devices during sleep to prevent teeth from grinding against each other. Mouth guards help to distribute the forces of grinding and clenching, reducing the pressure on the teeth and jaw joints. They can also help to alleviate associated symptoms such as headaches and jaw pain.
Medications
Muscle relaxants can help to relax the muscles involved in teeth grinding and clenching. These medications work by reducing muscle tension and promoting relaxation, which can reduce the intensity of bruxism episodes.
However, it is important to note that these medications should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as they may have side effects and can be habit-forming.
Botulinum Toxin Injections
botulinum toxin injections. Botulinum toxin, commonly known as Botox, can be injected into the muscles responsible for clenching and grinding.
By temporarily paralyzing these muscles, Botox can reduce the intensity of bruxism episodes and provide relief from associated symptoms. This treatment is typically reserved for severe cases of bruxism or when other treatments have been ineffective.
Coping and Preventing Bruxism
Bruxism can be both physically and emotionally distressing. However, by implementing effective coping mechanisms and preventive measures, individuals can effectively manage this condition.
Handling Jaw Pain
Regularly applying warm compresses to the jaw area can help relieve muscle tension and reduce pain.
Additionally, practicing jaw exercises recommended by a healthcare professional or physical therapist can strengthen the muscles surrounding the jaw joint, potentially reducing discomfort associated with bruxism.
Improving Sleep Hygiene
Establishing a consistent sleep schedule and creating a relaxing evening routine can contribute to better quality sleep. Avoiding caffeine and electronic devices before bed can also promote a restful sleep environment.
Additionally, individuals with bruxism may benefit from using relaxation techniques before bed, such as deep breathing exercises or listening to calming music.
Know more about how to improve your Sleep Hygiene.
Stress Management
Since stress is often a trigger for bruxism, finding healthy ways to cope with stress can significantly reduce its occurrence. Engaging in activities such as exercise, meditation, or hobbies that promote relaxation can help alleviate stress levels and decrease the likelihood of teeth grinding.
Know more about the relationship between Stress and Insomnia.
Addressing the Underlying Causes
If stress is the main trigger, seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor can provide valuable guidance on stress management techniques.
Additionally, visiting a dentist who specializes in treating bruxism can help identify any dental issues that may be contributing to the condition and provide appropriate treatment options.
FAQs
How common is bruxism?
It is estimated that around 10–20% of adults and children suffer from bruxism to some degree. While the exact cause of bruxism is unknown, it is believed to be related to factors such as stress, anxiety, misaligned teeth, or sleep disorders.
Is bruxism a serious medical condition?
While it may not be considered a life-threatening medical condition, it can have serious consequences for oral health and overall well-being. Bruxism can result in worn-down teeth, jaw pain, headaches, and even damage to the temporomandibular joint (TMJ). In severe cases, it can lead to tooth fractures or loss. Additionally, bruxism has been linked to sleep disorders and can disrupt a person's quality of sleep.
How does bruxism affect sleep?
The constant grinding can lead to various sleep disruptions, such as frequent awakenings, difficulty falling asleep, and even sleep apnea. Bruxism causes muscle tension and discomfort, which can make it challenging for individuals to find a comfortable sleeping position. Additionally, the grinding sound itself can disturb both the person experiencing bruxism and their sleep partner.
How is bruxism diagnosed?
Diagnosing bruxism is a thorough examination by a dentist or dental specialist. They will look for signs of teeth grinding, such as worn tooth surfaces, jaw pain, and muscle tenderness. They may also ask about symptoms such as headaches, earaches, and sleep disturbances, as these can be associated with bruxism. Additionally, the dentist may inquire about any stress or anxiety that the patient may be experiencing, as these can contribute to bruxism.
Conclusion
Bruxism is a common condition that affects many individuals. It is characterized by the grinding or clenching of teeth, often during sleep. The consequences of bruxism can be detrimental to oral health, leading to tooth damage, jaw pain, and headaches.
Therefore, it is crucial for individuals who suspect they may have bruxism to seek professional help for diagnosis and treatment. Options for managing bruxism include wearing a mouthguard at night, practicing stress-reducing techniques, and addressing any underlying dental issues.
By taking proactive measures, individuals can effectively manage bruxism and improve their overall oral health.
Jessica H.
Jessica is a reviewer, writer, and sleep enthusiast at Sleepiverse. Jessica graduated with her master's degree in Nursing research and education. She is a registered nurse and currently works in the Intensive Care Unit. Since becoming a nurse, Jessica has worked the night shift, which means a disrupted sleep schedule. Knowing she needed to function at her best while caring for patients at night, she spent a lot of time researching how to sleep well with a difficult schedule.


